You may be considering buying an omnidirectional antenna and think their either a fad or a scam. Well below ill go through all their benefits and drawbacks. These types of antennas are not just a fad. They do serve a specific purpose. They may be just what you need depending on a few factors.
Getting Started
An omnidirectional antenna is characterized primarily by its signal pickup in all directions. The 360-degree signal reception allows for versatility. Contrary to how a directional antenna works, an omnidirectional antenna should not point to a specific location.
No matter where the signal transmitter is located, this omnidirectional antenna can pick up the signal without any inconvenience.
Why Omnidirectional Antennas Work
- Wide Coverage Area: Omnidirectional antennas are designed to pick up signals from all directions, which makes them ideal for use in locations where the transmitter is located at an unknown or variable distance.
- No Need for Precise Aiming: Unlike directional antennas, which need to be pointed accurately in the transmitter’s direction, omnidirectional antennas do not need to be aimed. This makes them easier to install and use.
- High Gain: Omnidirectional antennas are typically designed to have a high gain, which means that they can amplify weak signals and improve the range and performance of the antenna.
- Multiple Devices: Omnidirectional antennas can provide coverage for multiple devices, such as TVs or computers, that need to access the same signal.
- Easy Installation: Omnidirectional antennas are relatively easy to install, as they do not require precise aiming or orientation.
It should be considered that these antennas offer shorter effective ranges than directional antennas.
One of the deficient aspects is the coverage of the omnidirectional antenna itself. Experts say that this particular antenna should not be installed too high. This antenna cannot be tilted downward like directional antennas. A medium height avoids inadequate coverage to some signal transmitters.
Omnidirectional antennas only provide short ranges. The average receiving distance range is usually between 20 and 30 miles. This is why it is indicated that this is a much more suitable antenna for cities.
Rural or too remote areas need to use a directional antenna instead of an omnidirectional antenna.
When Should You Use an Omnidirectional Antenna?
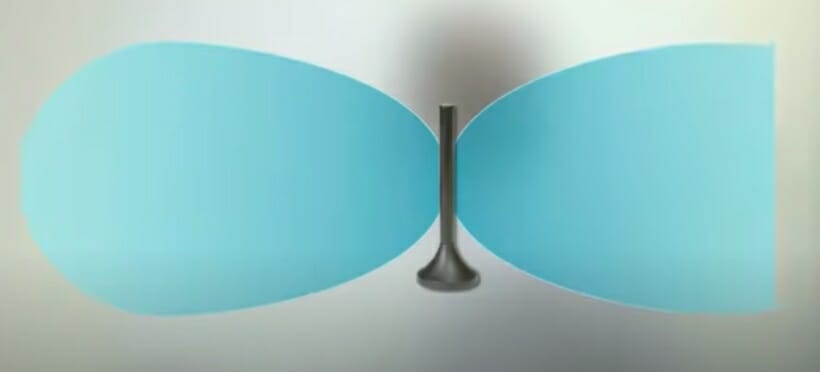
An omnidirectional antenna can be handy for people living in the city, as mentioned above. It is also an excellent antenna for the following cases:
- Moving vehicles like RVs: We can include recreational vehicles, campers, or boats.
- Tourist complexes: This includes clubhouses, hotels, campgrounds, and restaurants.
- In a location with a clear line of sight to the transmitter: Omnidirectional antennas are most effective when they have a clear line of sight to the transmitter, allowing them to pick up the strongest possible signal.
- In a location with a weak or variable signal: Omnidirectional antennas are well-suited for use in locations where the signal is weak or variable, as they can pick up signals from multiple directions.
- In a location with multiple transmitters: Omnidirectional antennas are ideal for use in locations with multiple transmitters, as they can pick up signals from all directions.
- In a location with multiple devices that need to access the same signal: Omnidirectional antennas can provide coverage for multiple devices, such as TVs or computers, that need to access the same signal.
If you want to create your own, you might want to check how to make an omnidirectional
Is a Directional or Omnidirectional Antenna Better?
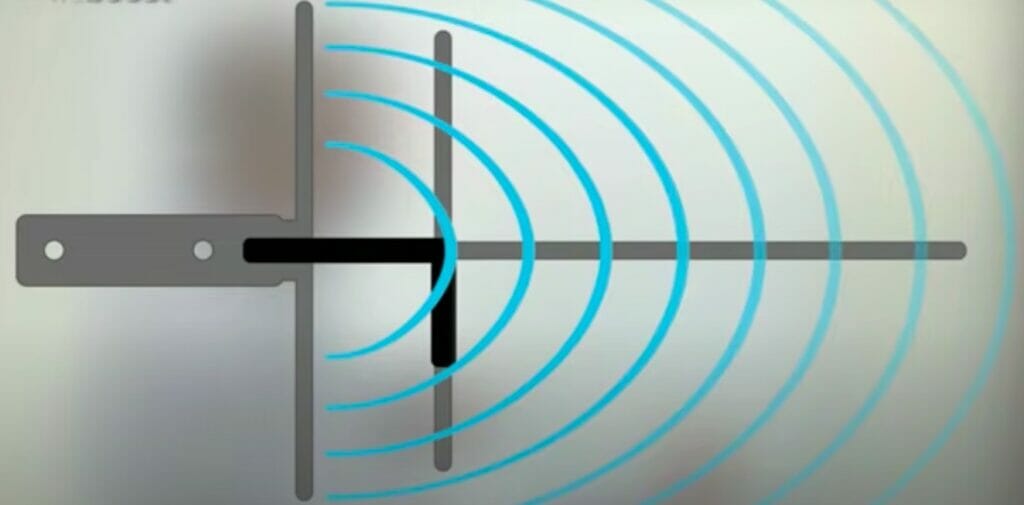
Each of these antennas provides different characteristics that can be tailored to each user depending on the area in which they live.

Directional TV Antenna (Pros)
- Can receive stronger signals from a specific direction
- Less prone to interference from other signals or physical obstructions
- Can be more effective at receiving signals from long distances
Directional TV Antenna (Cons)
- It needs to be pointed accurately in the direction of the transmitter.
- It may have a limited coverage area.
- It may require more precise installation and alignment.
Omnidirectional TV Antenna (Pros)
- Can receive signals from multiple directions
- It does not need to be pointed in a specific direction.
- Can provide coverage for multiple devices
- Easy to install
Omnidirectional TV Antenna (Cons)
- It may receive weaker signals than a directional antenna.
- More prone to interference from other signals or physical obstructions
- It may not be as effective at receiving signals from long distances.
Omnidirectional antennas are suitable for most users today. These antennas provide adequate coverage in all directions. A high level of RF energy is required.
Directional antennas are the right choice for rural areas as they can be oriented in a precise direction. This operation allows directional antennas to focus on a single location instead of covering the whole area like omnidirectional antennas. (1)
This particular feature means directional antennas will reach much farther than omnidirectional antennas. The disadvantage is that this can be done with only one provider or signal transmission.
The antenna must be moved in the appropriate direction for other signal transmissions. (2)
Wrapping Up
Omnidirectional antennas are the most convenient solutions for people who want to enjoy multiple TV signals in their homes. They are also an excellent option for moving vehicles, resorts, and ATMs. Several base stations, such as police or cab dispatchers, need an omnidirectional antenna to perform all their activities. (3)
References
(1) high level of RF energy – https://www.who.int/pehemf/meetings/archive/en/keynote5dawoud.pdf
(2) signal transmissions – https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/signal-transmission
(3) ATMs – https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/other/automated-teller-machine-atm/
Video Reference
weBoost

